Slow Loris
Slow Loris
Slow Loris
Do you know about an animal called Slow loris which moves very slowly? Slow lorises are a species of cute-looking monkeys that live in tropical rainforests such as India and Indochina. They are popular as pets in various countries due to their cute appearance. In this article, we will take a look at what characteristics and secrets slow lorises have in their lives!
Slow Loris Basic Infomation
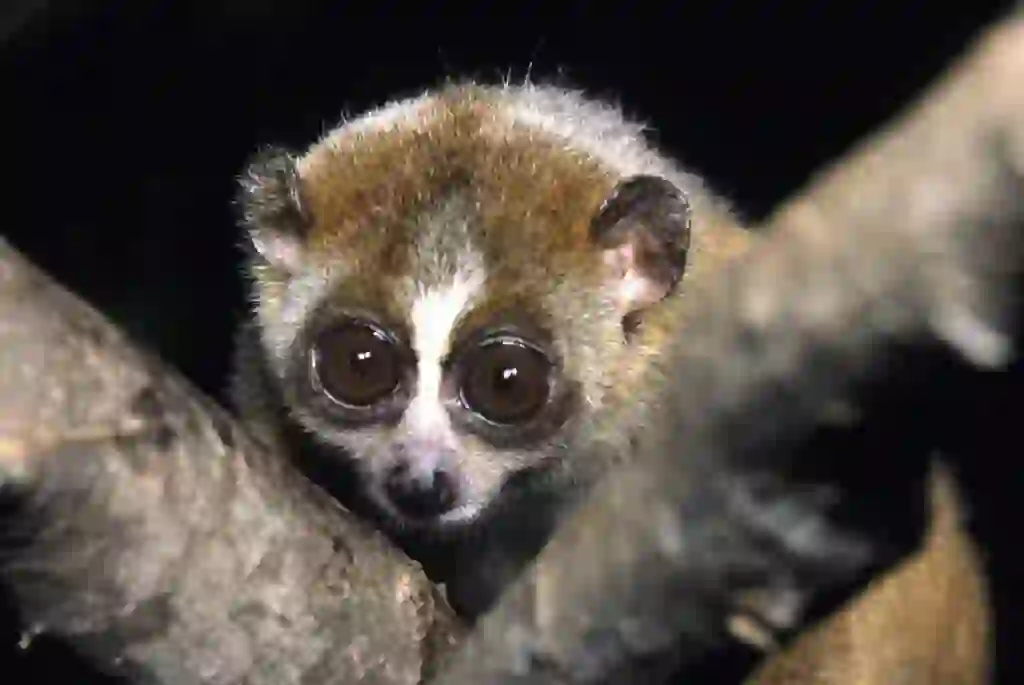

Mammalia-Primates-Lorisidae.
Length 10~30cm. Weight 230~1200g.
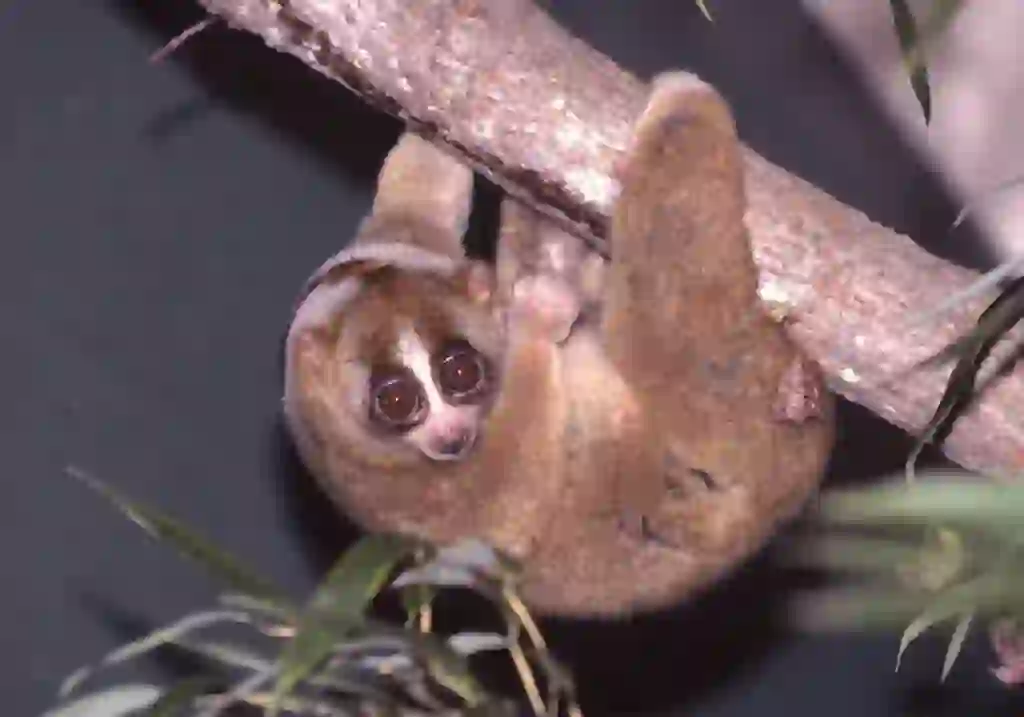
Slow lorises are a primitive species of monkey that live in tropical rainforests such as India and Indochina. They are nocturnal animals that mainly come out at night and sleep during the day by curling up on tree branches or hiding in the shadows. They are arboreal animals that live on trees and rarely come down to the ground.
Slow lorises have a cute, stuffed-animal-like appearance with small ears and a flat face. Their eyes are round and large. They have short and dense hair that grows all over their body, ranging in color from pale gray to reddish-brown.
They have a distinctive white line from their nose to their forehead and dark colors around their eyes like glasses. Unlike other monkeys that live on trees, they have almost no tail.
Slow lorises reach sexual maturity at around 17-21 months of age and can reproduce.
After reaching sexual maturity, slow lorises give birth every 12-18 months when food is abundant. The gestation period is about 190 days, and they usually give birth to one offspring per birth, occasionally two. The offspring are weaned at around 6 months of age.
Slow Loris Q&A

Where does slow loris get its name?
In fact, slow loris moves slowly, and it is said that the "slow" of slow loris comes from here. They dare to move slowly so as not to be spotted by natural enemies and prey.
There are various theories about the origin of "loris", but it is said that the etymology may be derived from a word that means "clown" or "slow-moving thing".
By the way, the scientific name of the slow loris is "Nycticebus coucang".

Why do slow loris live there?
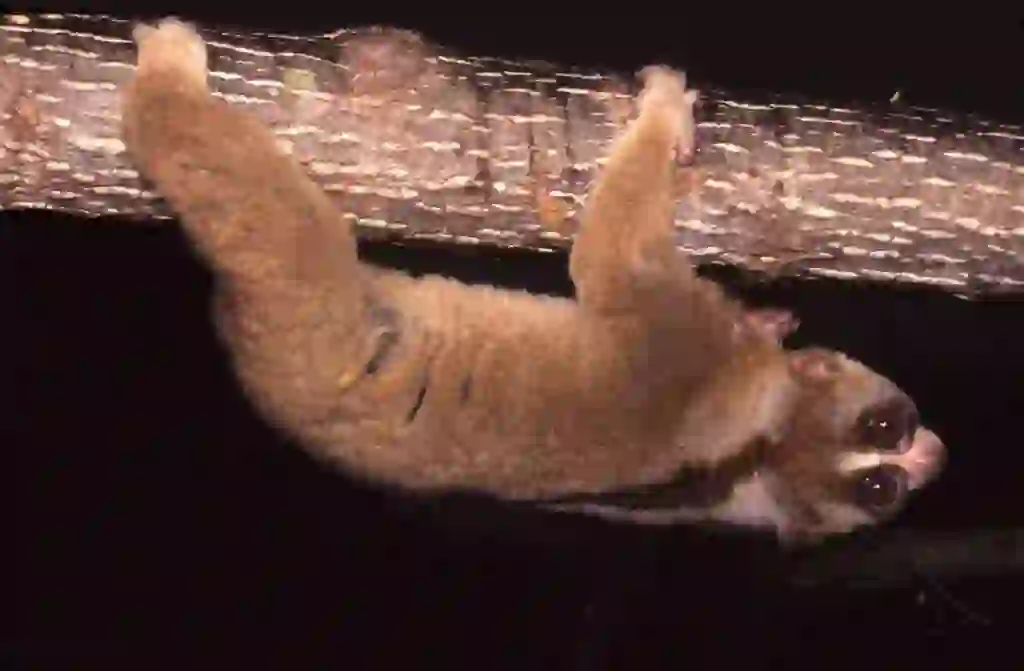
Slow lorises are found in India, Indochina, the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Java and Borneo. The exact reason why slow lorises inhabit these regions is unknown at this time.
However, these regions have many rich tropical rainforests with plenty of food and hiding places for slow lorises to live comfortably.

What does slow loris eaten?
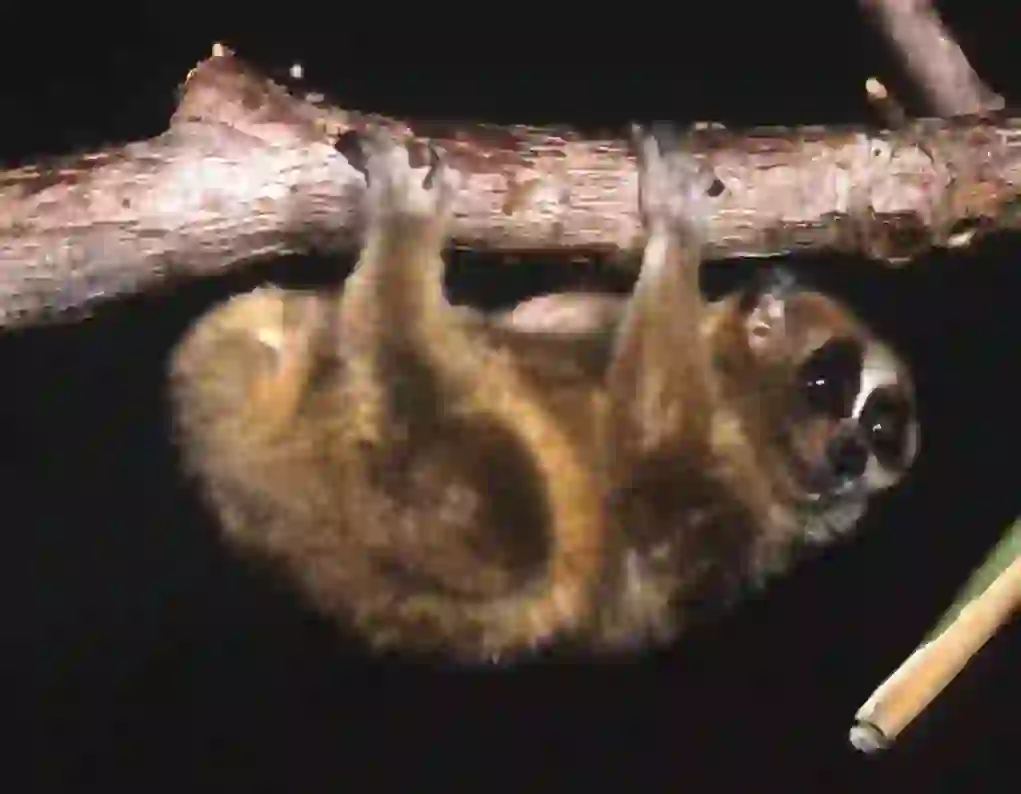
Slow lorises are omnivorous animals that eat fruits, plant seeds, sap and insects, as well as bird eggs and chicks. In zoos, they are often fed fruits (such as bananas and apples) and vegetables (such as carrots and sweet potatoes), pellets for primates, and insects (such as crickets, mealworms and grasshoppers).
However, research on slow lorises has progressed and it is now believed that slow lorises living in the wild eat more sap and honey than fruits. They eat less fruit than previously thought.
Therefore, some zoos try to improve the diet of slow lorises as much as possible to keep them healthy. They give them sap and gum (acacia sap) to get closer to their natural diet.

What animal is the slow loris?
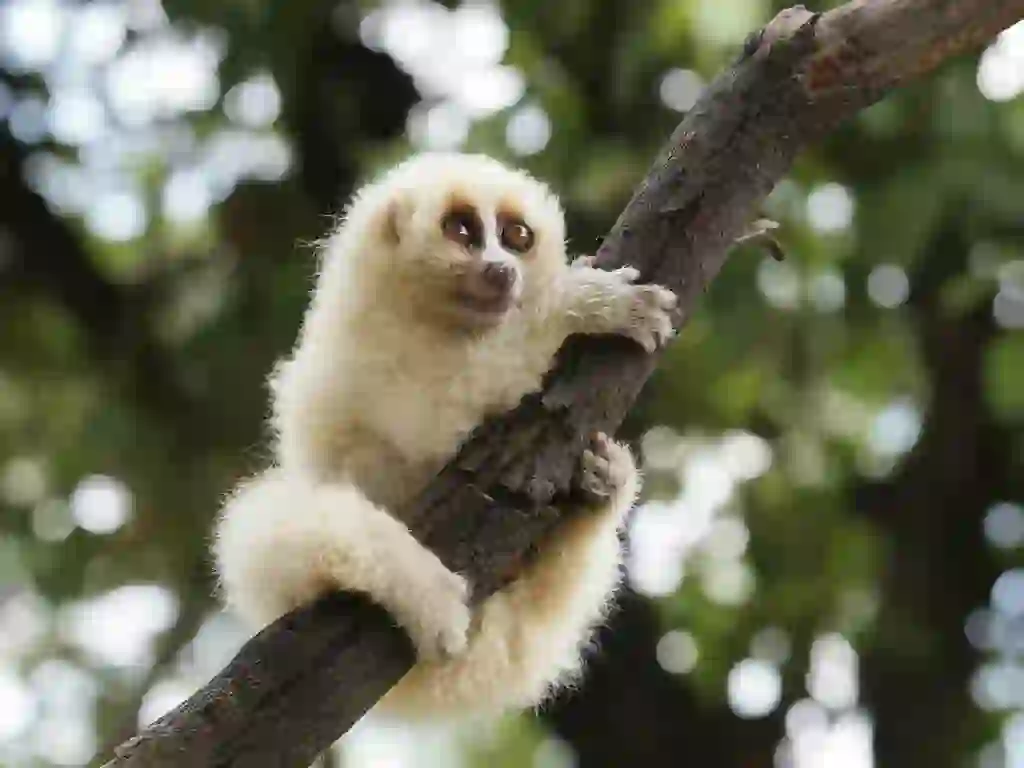
Many people mistakenly believe that slow lorises are a type of squirrel because of their round face and eyes and their name “loris”.
However, slow lorises are a type of “prosimian” primitive monkey, such as the tarsier and the lemur. They are a proud member of the monkey family.
By the way, the slow loris has five fingers just like us humans, and the second toe (index finger) of its foot has a hook claw for grooming and ear cleaning. As an animal that lives in trees, it has a strong grip and can hang on to tree branches with only its hind legs.
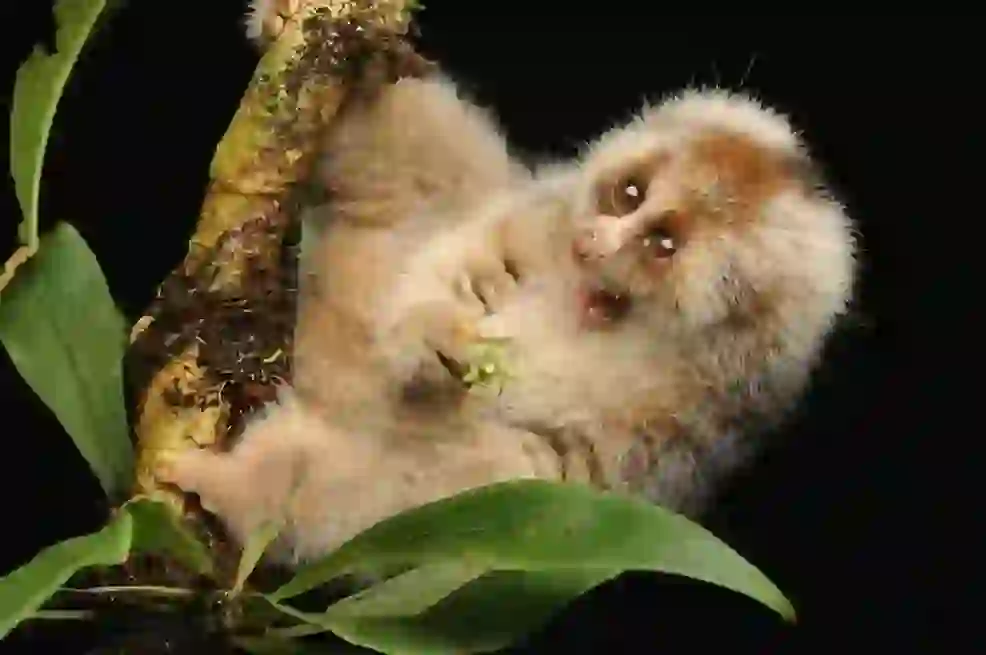

What kind of personality does slow loris have?
Slow lorises are known for their timid and shy nature.
They are easily stressed and are prone to stress-related illnesses such as stomach ulcers. However, young individuals (around 1-2 years old) are often more aggressive and may confront others with quick movements
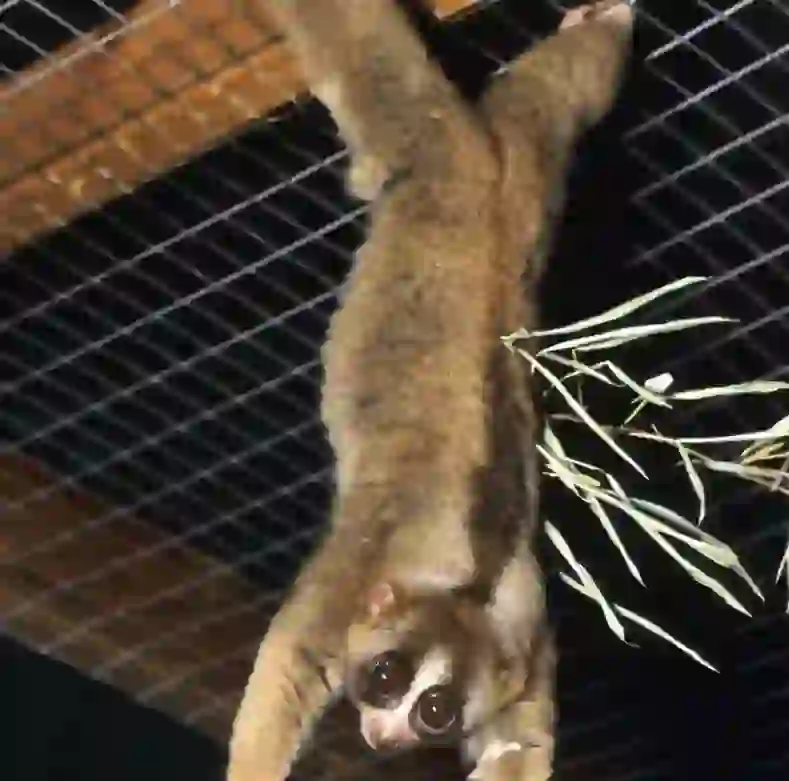

Is it true that slow loris are poisonous?
It's true.
Slow loris is known as "the only primate that has venom".
The venom of the slow loris is contained in saliva, but it is also secreted by the venom glands located on the inside of the elbow. And if you mix saliva with poison secreted by the venom glands on the inside of your elbow, it becomes even more toxic.
When a slow loris is attacked by a natural enemy, it repels natural enemies by biting it with teeth smeared with this strong poison.
In addition, the mother of the slow loris leaves the young in the nest and goes in search of food, but when they are separated from the young, they have a habit of smearing poison on the child's body to protect it from predators.
When we humans are bitten by a slow loris, we may experience mild allergy-like symptoms (itchy eyes and nose, hives), and if it becomes severe, it can be life-threatening.
By the way, slow loris can decompose poison with its own digestive organs, so it will not cause poisoning with its own poison.
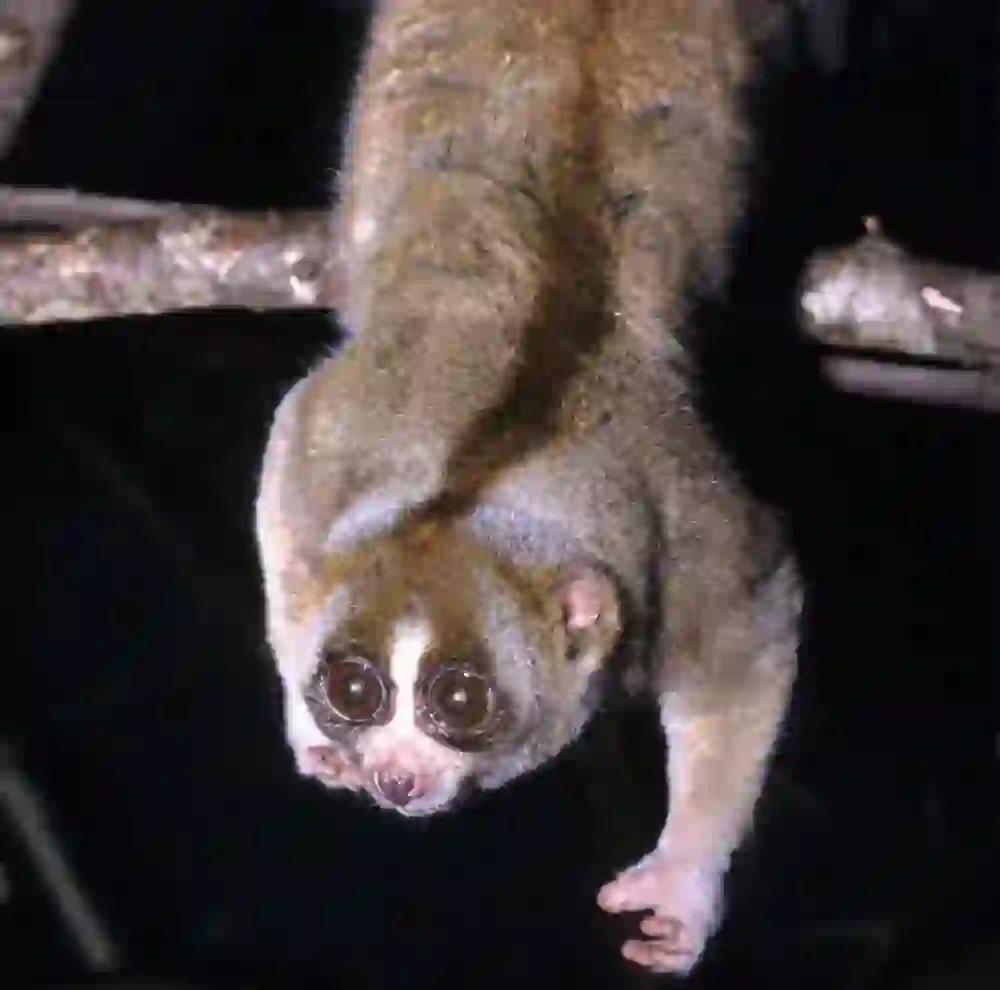

Can slow loris be kept as pets?
When breeding rare animals at home, it is necessary to follow the established laws in some countries. This time, we will introduce whether you can breed slow loris at home in Japan.
In conclusion, slow lorises are difficult to obtain and it is difficult to keep them as pets.
But it's not impossible. When keeping a slow loris as a pet, it is a good idea to feed it with monkey pellets as the main food, various vegetables, fruits, insects and eggs.As I wrote earlier, getting a slow loris right now is not easy. However, in the past, slow loris were not so rare.
In fact, due to their cute appearance, slow lorises became popular as pets around the world and began to be over-harvested. As a result, their population in the wild has decreased. It was judged that there was a high possibility of extinction if this continued, and in 2007 commercial transactions were generally prohibited.
However, it is possible to transfer ownership of individuals that have been imported or bred through proper procedures and have been properly registered under the Species Conservation Act along with their registration certificate. However, it is often smuggled into the country illegally because going through the proper procedures is very time-consuming and expensive.
Note that while slow lorises have individual differences, some individuals become very attached to humans. However, there are also many individuals that do not become attached at all and bite people immediately.
Therefore, it is said that slow lorises kept as pets are often toothless so that they do not bite humans. Toothless slow lorises often die from infections and even if they survive, they cannot return to the wild and end their lives.
Slow lorises are very cute animals, but they are not animals that have been improved for pets. They are wild animals. If you are considering keeping a slow loris as a pet, please consider whether you really need to keep a wild animal or whether you really need a slow loris.
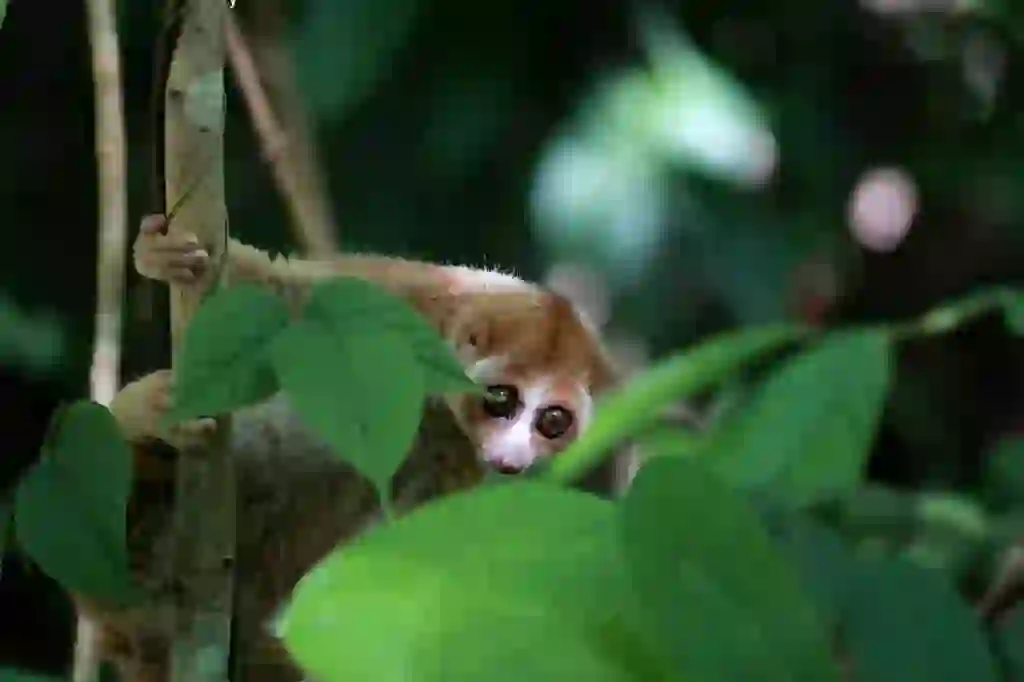

Is there a place to see slow loris in Japan?
Pygmy slow lorises are kept at the “Ueno Zoo” in Tokyo and the “Kyoto City Zoo” in Kyoto, greater slow lorises are kept at the “Maruyama Zoo” in Sapporo, Hokkaido.
In fact, most of the slow loris bred in zoos have been illegally imported and found at customs and have nowhere to go.
They are forcibly brought out of their original habitat to be kept as pets, and eventually they have nowhere to go. I can only hope that such sad slow loris can be reduced as much as possible.
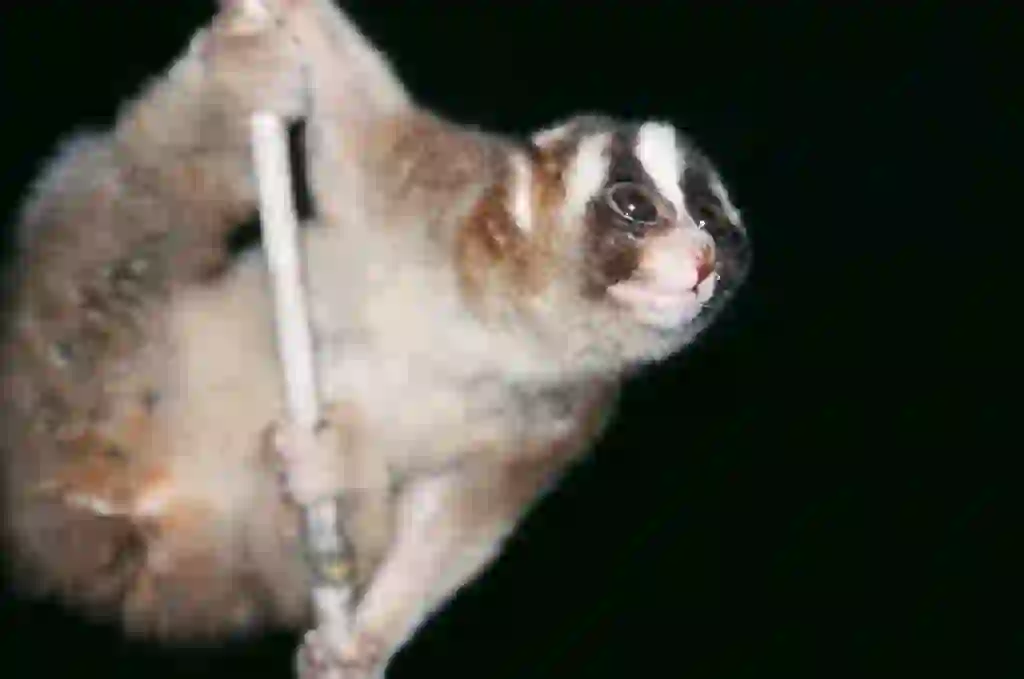

What is the lifespan of a slow loris?
The lifespan of a slow loris is believed to be about 20 years.
However, slow lorises are weak to stress and often become ill due to minor changes in their environment. It is not easy to live a full life under stressful conditions where environmental changes are likely to occur.
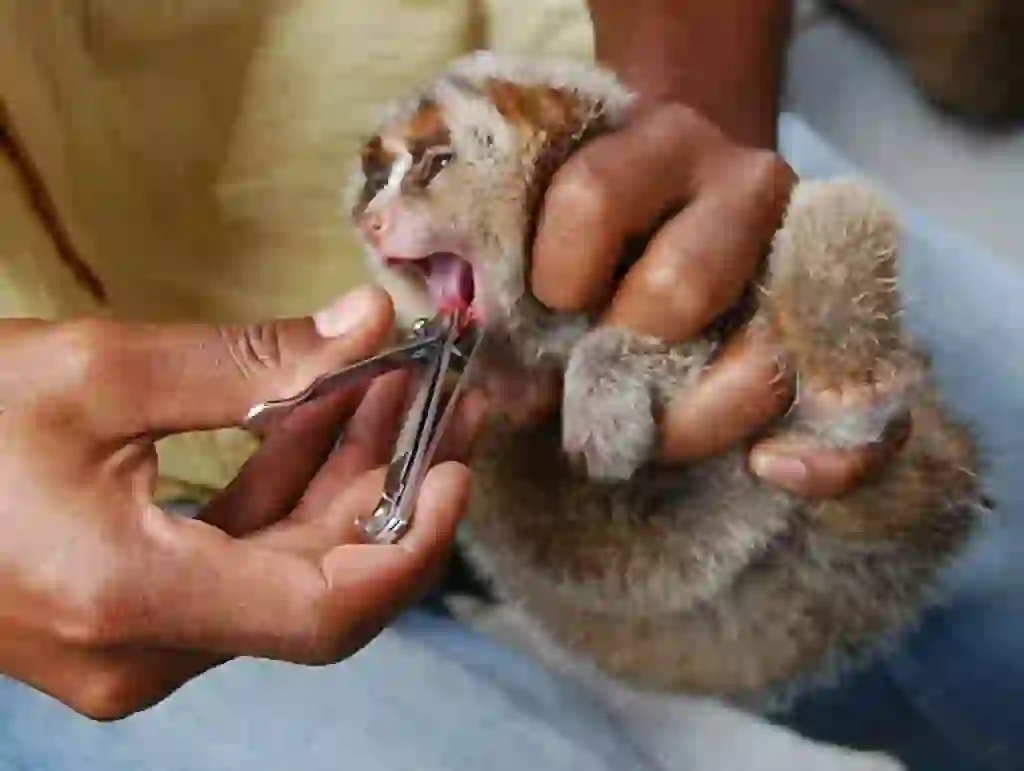
What enemies does slow loris have?
The natural enemies of slow loris in the wild are large snakes such as pythons, birds of prey such as golden eagles, orangutans and monitor lizards.
But for slow loris, our biggest enemy is us humans.
Slow lorises are protected worldwide, but are illegally captured and exported due to high demand as pets. They are also sometimes captured for use as raw materials for traditional Chinese medicine or for food. In addition, their habitats are destroyed by deforestation and the effects of war, putting all slow lorises at risk of extinction.。
All species of slow lorises are classified as “Appendix I” under the Washington Convention because they are affected or likely to be affected by trade as species threatened with extinction. Animals classified as Appendix I are protected worldwide and cannot be traded between countries unless there is a special purpose such as research.
Also, the javan slow loris is classified as “CR” (Critically Endangered), the bengal slow loris, greater slow loris and pygmy slow loris are classified as “EN” (Endangered), and the bornean slow loris is classified as “VU” (Vulnerable) on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List.

Would you like to become a part of the 'Animalbook.jp'?
Turn your knowledge into Q&A and share it with the world. ※Publication will be activated after purchase. Let's share information together!
Slow Loris Type of List
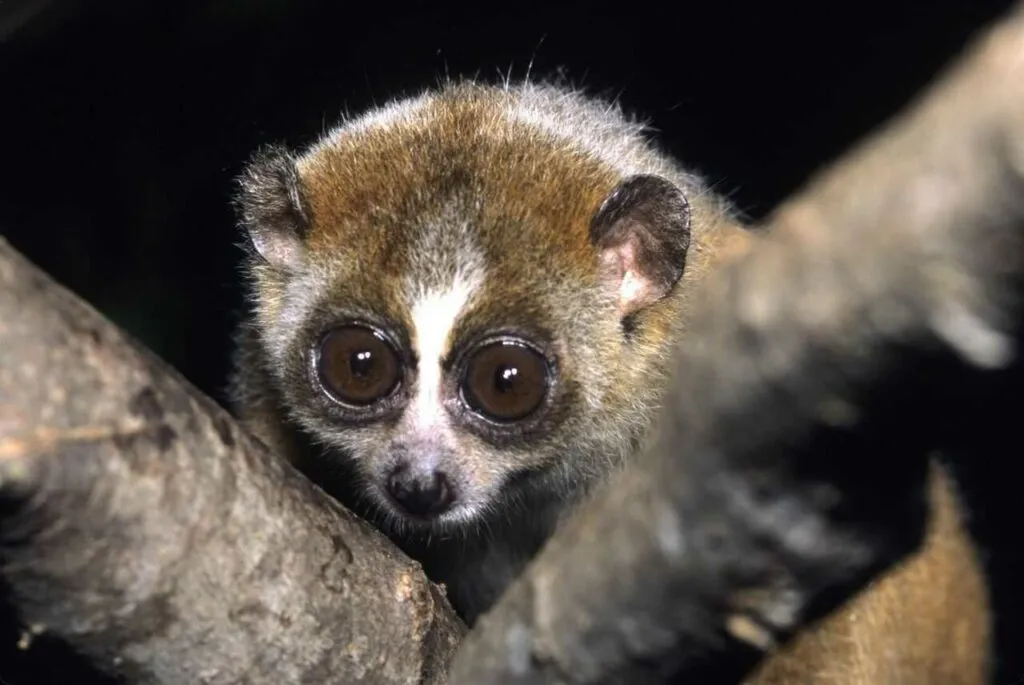

・Bengal Slow Loris ・Greater Slow Loris ・Javan Slow Loris ・Bornean Slow Loris ・Pygmy Slow Loris etc.
※The classification varies from researcher to researcher.
Information
Congratulations! You are the first commenter!

Create Your Favorite List!
Slow Loris
Save the animals you love! Build your own list to quickly revisit your favorites later.

Would you like to leave a comment?
※Please note: This is for the purchase of rights to post comments within the article.
Find Your Favorites!
Our shop offers a unique and attractive selection of goods themed around various animals.
Slow Loris References

- 認定NPO法人 野生生物保全論研究会(JWCS) https://www.jwcs.org/data/JWCSshikibetuLoris.pdf
- 特定非営利活動法人 野生生物保全論研究会(JWCS)「スローロリス類登録事務に関する要望書」 https://www.jwcs.org/data/070908.pdf
- 環境省「スローロリスは野生動物です」 https://www.env.go.jp/nature/yasei/slow_loris/leaflet080522.pdf
- 認定NPO法人野生生物保全論研究会(JWCS)「改正・種の保存法が6月1日から施行」 https://www.jwcs.org/now/821/
- 札幌市円山動物園「スンダスローロリス」 https://www.city.sapporo.jp/zoo/024-e.html
- 札幌市円山動物園「スローロリス」 https://www.city.sapporo.jp/zoo/red_data_book/mammalia_06.html
- 札幌市円山動物園「臨時休園特別動画「今日の円山動物園」追加情報【スンダスローロリス】」 https://www.city.sapporo.jp/zoo/03doubutsu/kangarookan/slowloris/20200318.html
- ナショナルジオグラフィック「スローロリスのかわいい顔 怖い意味があった」 https://natgeo.nikkeibp.co.jp/atcl/news/19/021300101/
- SHAPE-Japan The Shape of Enrichment日本支部「ロリスの餌と健康の関係~ゴム(Gum)で歯の健康を守る?~」 http://www.enrichment-jp.org/2015/10/25/loris_food_health/
- 熊本市「水辺の動植物園 動植物園だよりvol.3」 https://www.city.kumamoto.jp/common/UploadFileDsp.aspx?c_id=5&id=24474&sub_id=1&flid=172698
- 静岡市立日本平動物園「でっきぶらし219号(2014年08月)5ページ 病院だより こころのケアも大切に」 https://www.nhdzoo.jp/newspaper/naka.php?newspaper_uid=2022&newspaper_num=219
Slow Loris Introduction of media used

出典:https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Coucang.jpg

food
出典:https://pixabay.com/images/id-1213041/
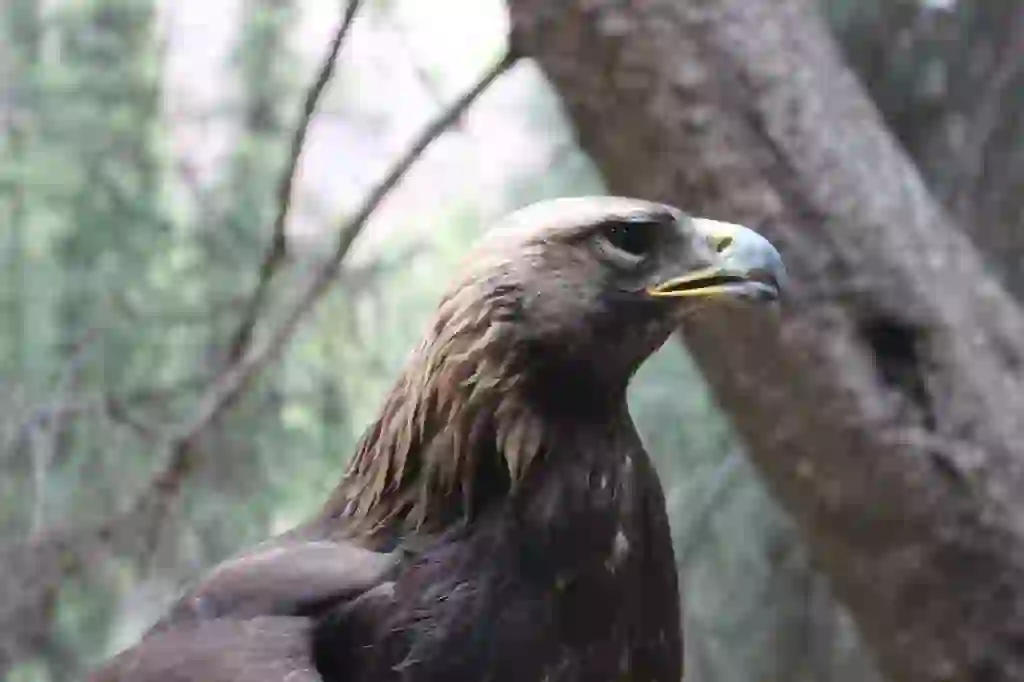

enemy
出典:https://pixabay.com/images/id-4266693/
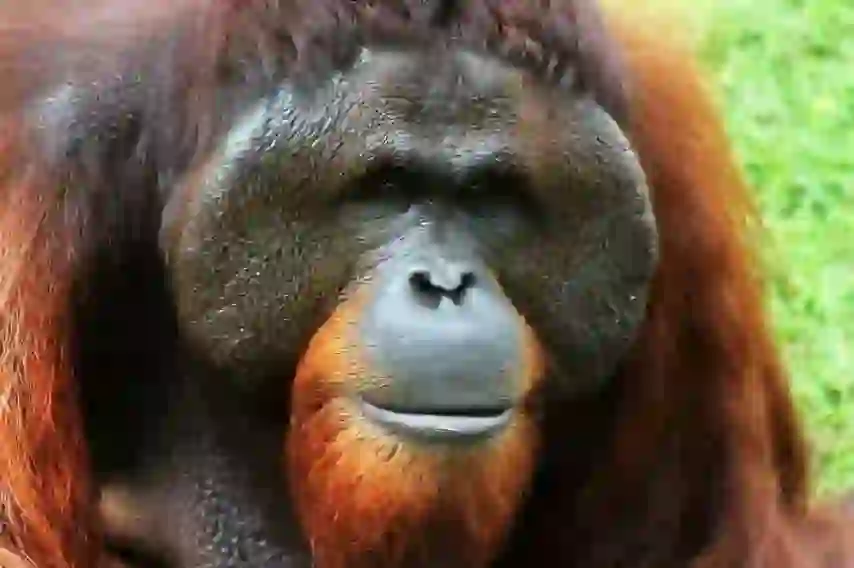

enemy
出典:https://pixabay.com/images/id-250664/

Help Enrich Our Animalbook.jp with Your Media!
We are constantly looking to expand and enrich our Animalbook.jp with amazing photos and videos of animals. If you have any media that you'd like to share, please contribute and help us showcase the beauty and diversity of the animal kingdom. Your submissions will be credited and featured in our encyclopedia, reaching a wide audience of animal lovers.





















