Clawed Frog
Clawed Frog
Clawed Frog
Meet the clawed frog, an unusual amphibian that spends its entire life underwater. As its name suggests, this frog has sharp claws on its hind feet! Let's dive into the fascinating world of these unique creatures, who play an important role as laboratory animals!
Clawed Frog Basic Infomation

| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pipidae |
| Taxonomic Status | FAMILY |
| Rank | Family |
| Vernacular Names | tongueless frogs |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Amphibia |
| Order | Anura |
| Family | Pipidae |

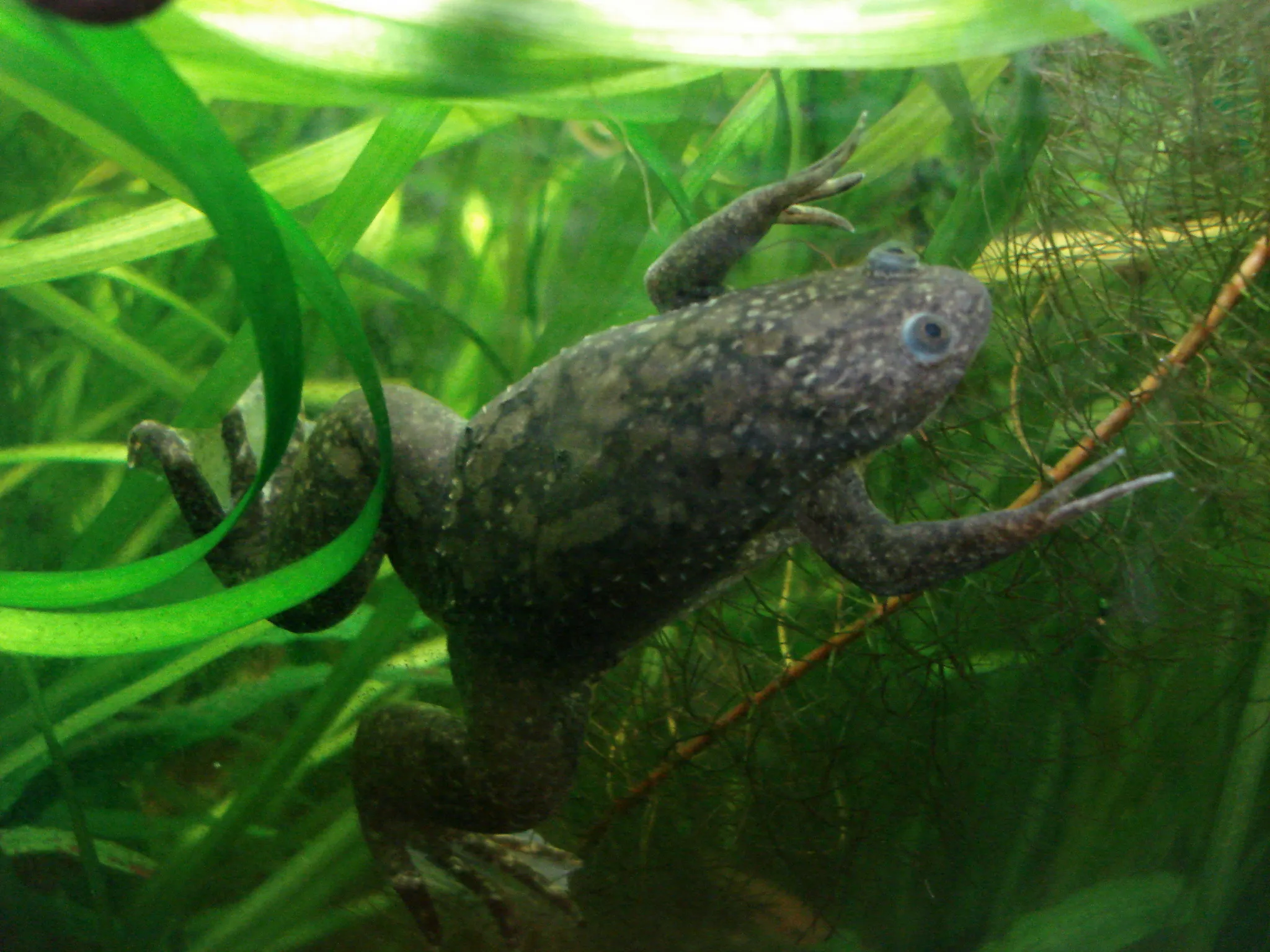
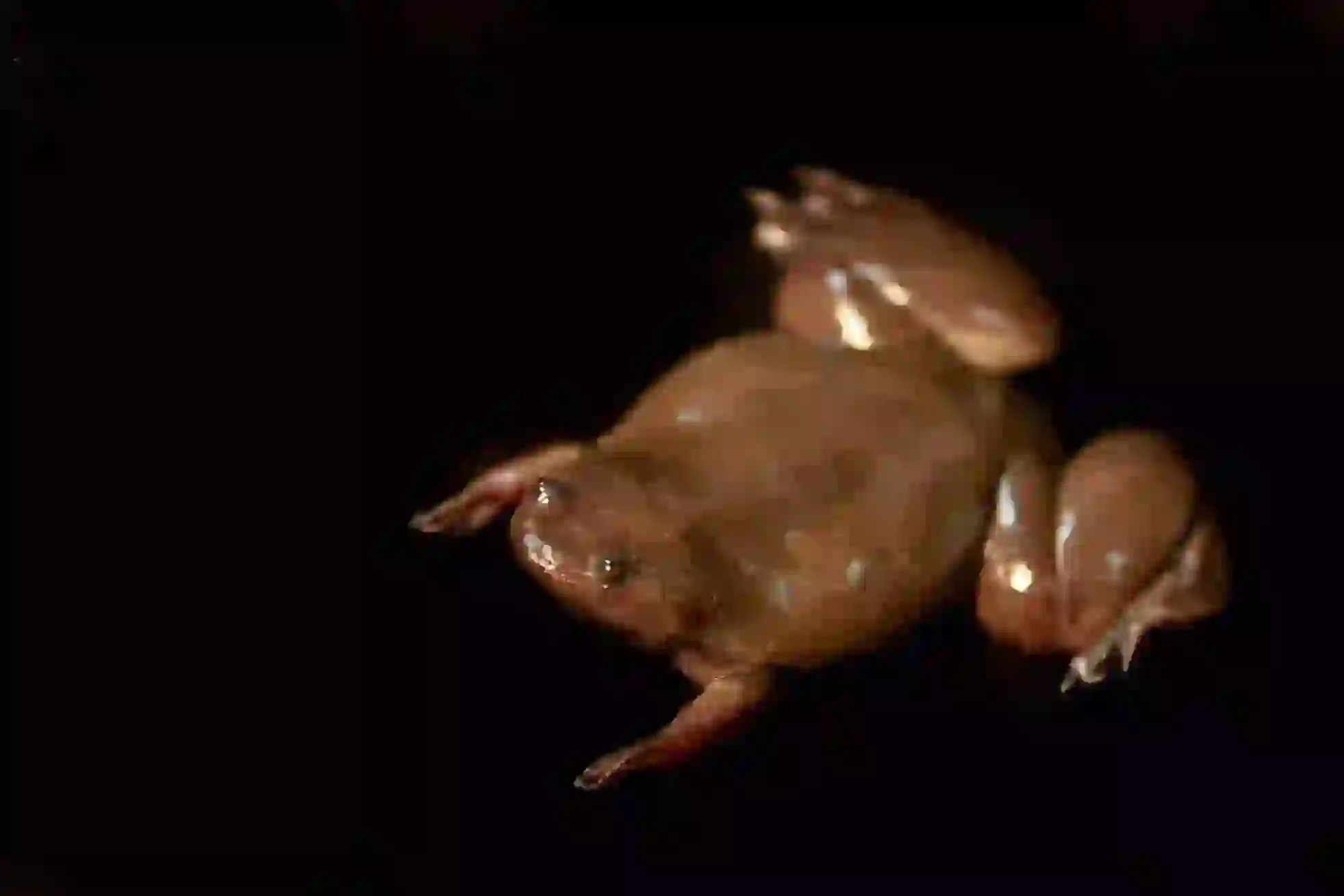
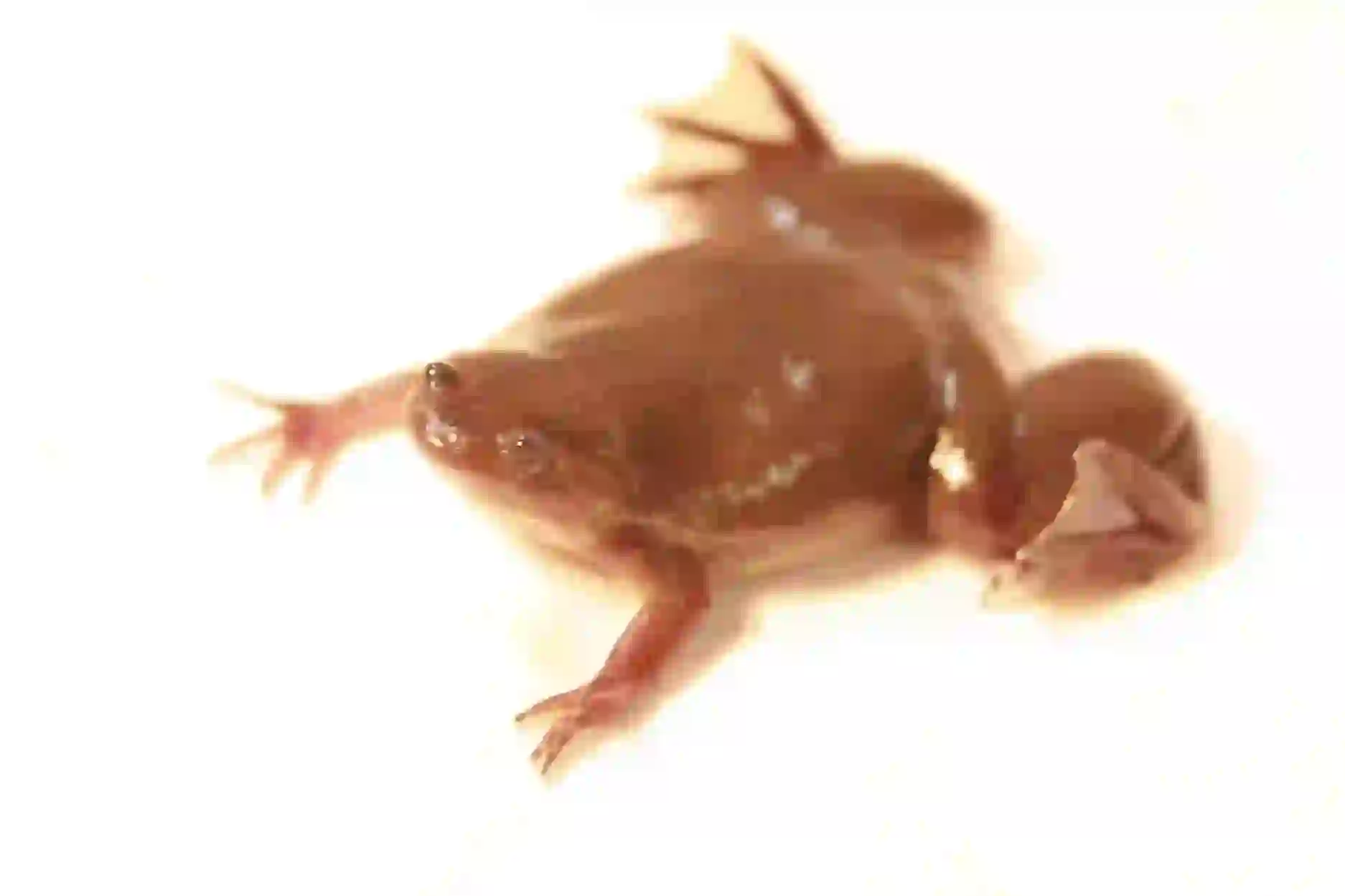
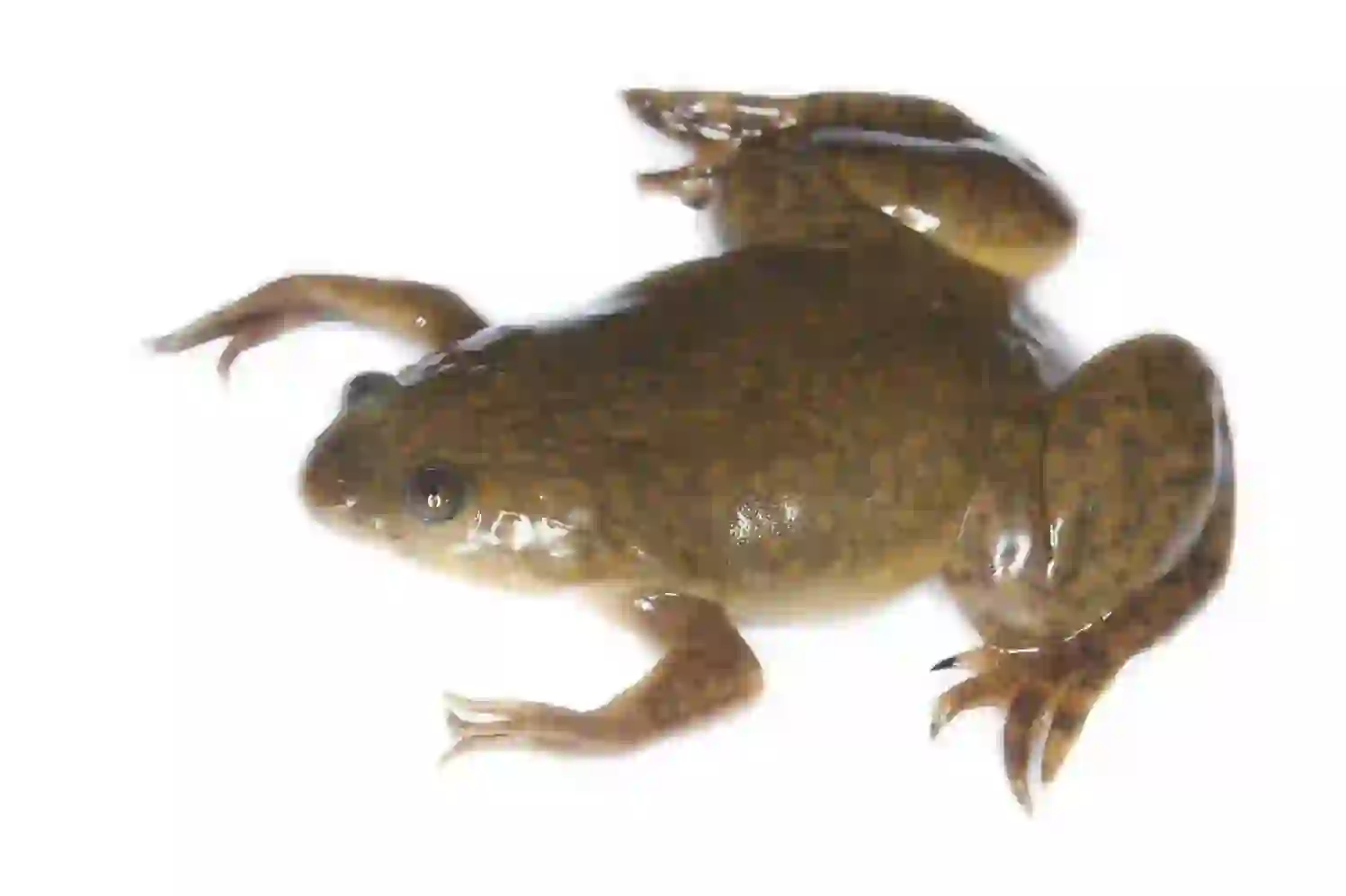
Clawed frogs are a group of frogs belonging to the family Pipidae, found primarily in Africa.
They typically range in size from 5cm to 12cm and are characterized by their flattened bodies and small heads.
Their namesake claws are sharp, black, and located on the three inner toes of their hind feet.
Clawed Frog Q&A

What kind of frog is a clawed frog?
Unlike most frogs, clawed frogs are fully aquatic, spending their entire lives in water.
Their skin is smooth and their body is streamlined for efficient movement underwater.
Their eyes are positioned on top of their heads, allowing them to observe their surroundings without having to surface.
Some species also secrete toxins from their skin as a defense mechanism against predators.

What are the claws of a clawed frog used for?
The claws on a clawed frog's hind feet are used to help them catch food in the water.
Clawed frogs primarily feed on aquatic insects, small fish, and crustaceans,
They use their claws to grasp these prey items firmly.
The claws also come in handy when digging through mud at the bottom of water bodies to find hidden food.
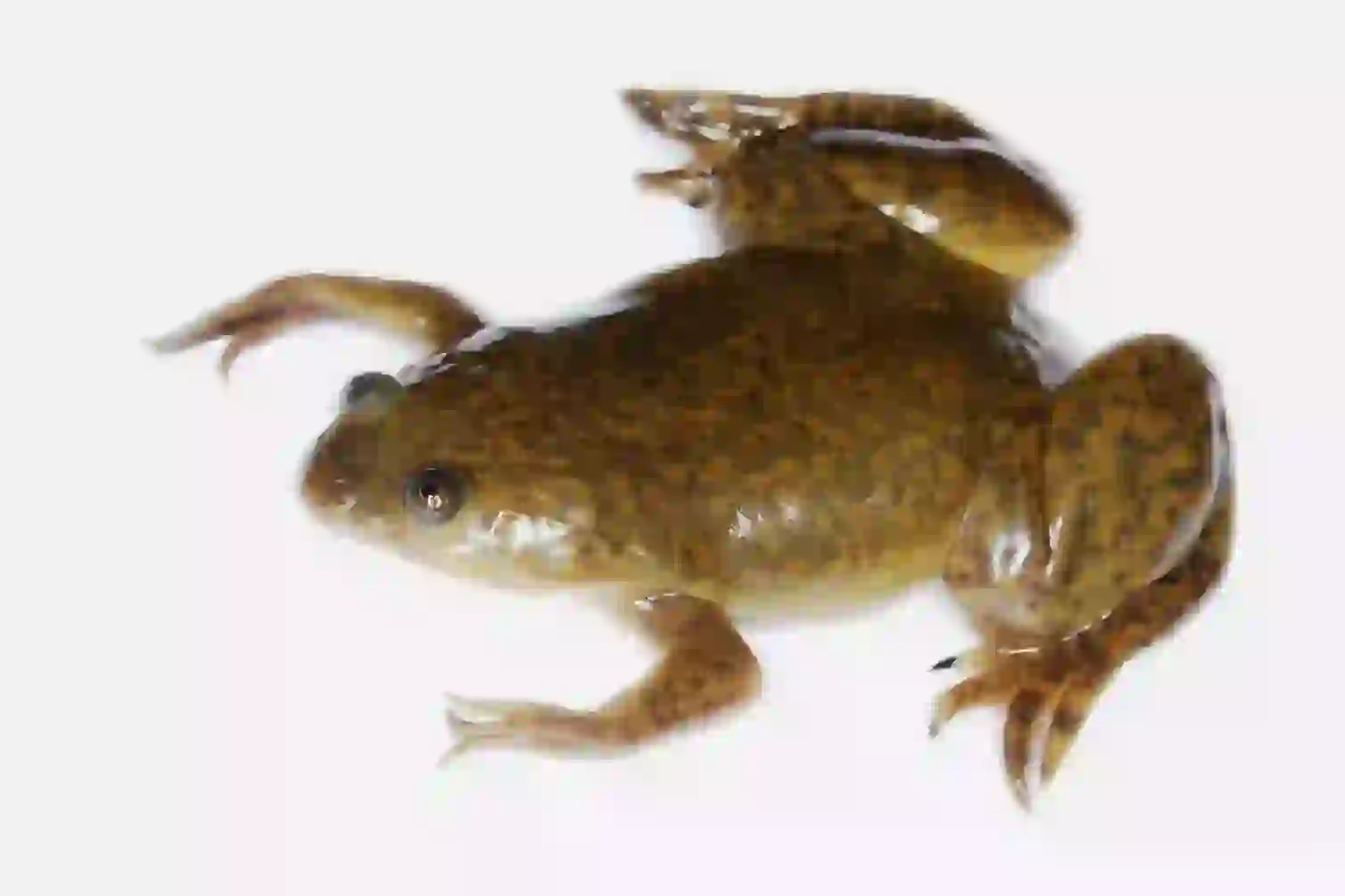

Why are clawed frogs used in research?
Clawed frogs are widely used in research in fields such as developmental biology and genetics because they are easy to breed, have high reproductive rates, and lay relatively large eggs.
The African clawed frog, in particular, is kept in research institutions around the world,
It has contributed to understanding the mechanisms of human diseases and the development of new drugs.

How do clawed frogs reproduce?
Clawed frogs breed in water during the rainy season.
Males produce unique vocalizations to attract females.
Females lay their eggs on aquatic plants, which are then fertilized by the males.
The eggs hatch within a few days, releasing tadpoles.
Tadpoles live in water and eventually undergo metamorphosis to become adults.

Can clawed frogs be kept as pets?
Clawed frogs are sometimes kept as pets because they are relatively easy to care for.
However, they are sensitive to water temperature and quality, so careful attention is needed when keeping them.
Also, clawed frogs are nocturnal, meaning they are not very active during the day.
Therefore, they may not be suitable for people who are looking for an active pet.

Would you like to become a part of the 'Animalbook.jp'?
Turn your knowledge into Q&A and share it with the world. ※Publication will be activated after purchase. Let's share information together!
Clawed Frog Type of List

・African Clawed Frog
・Dwarf Clawed Frog
Congo Dwarf Clawed Frog
Information
Congratulations! You are the first commenter!

Create Your Favorite List!
Clawed Frog
Save the animals you love! Build your own list to quickly revisit your favorites later.

Would you like to leave a comment?
※Please note: This is for the purchase of rights to post comments within the article.
Find Your Favorites!
Our shop offers a unique and attractive selection of goods themed around various animals.
Clawed Frog References
Clawed Frog Introduction of media used

I, Pouzin Olivier, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons

Slc8l, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons

Brian Gratwicke, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons

Marius Berger, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons

Lennart Hudel, CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons

Brian Gratwicke, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons

Brian Gratwicke, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Brian Gratwicke, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons

Oliver Angus, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
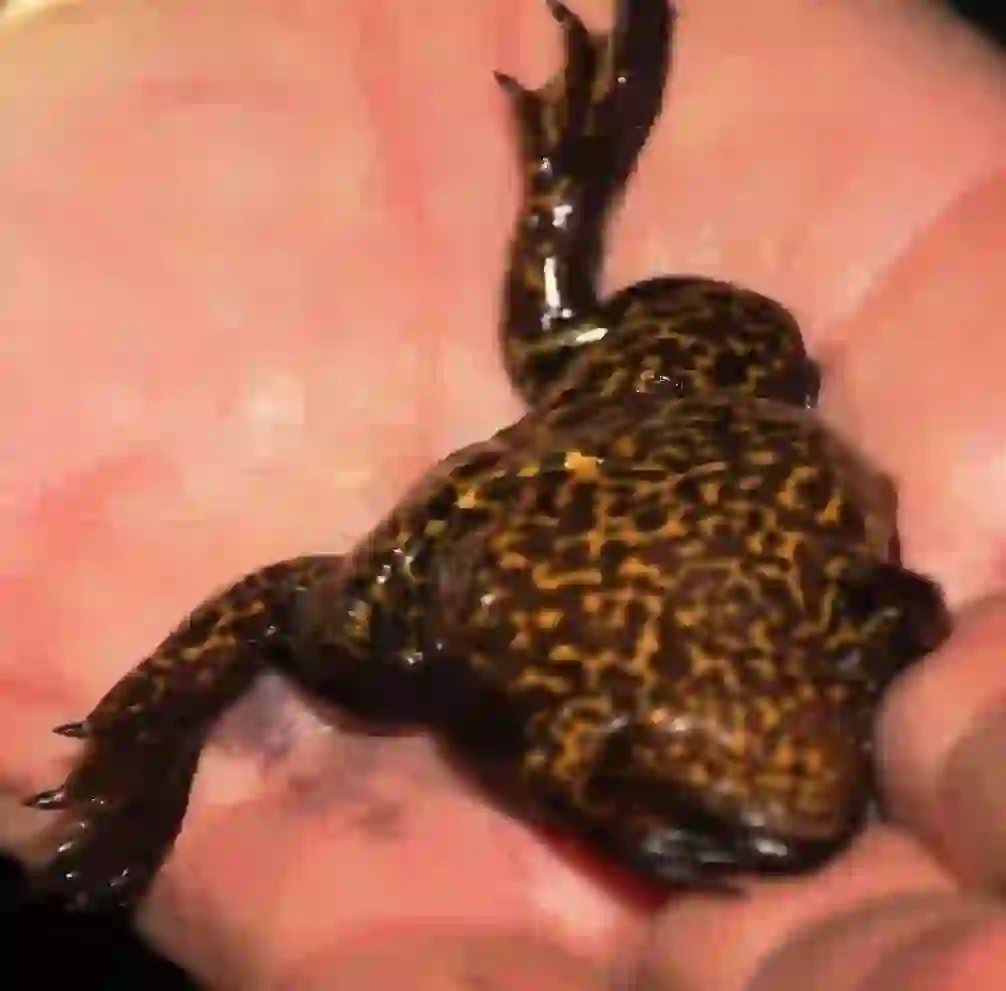

Tony Rebelo, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
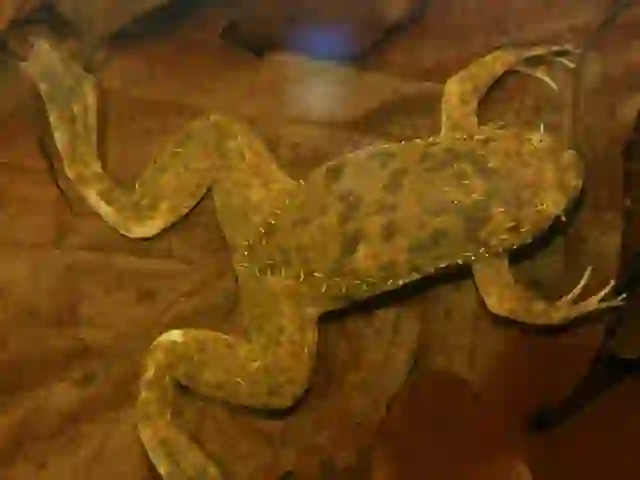

Václav Gvoždík, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
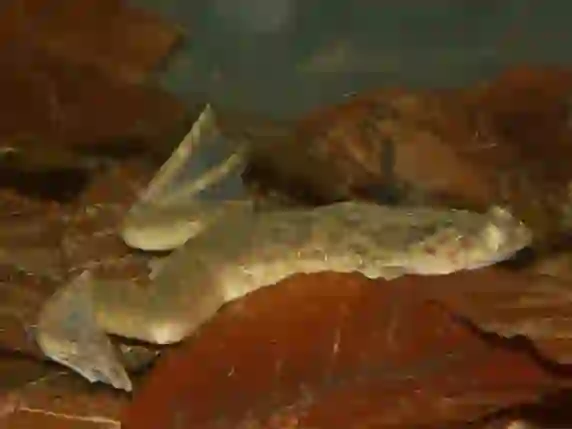

Václav Gvoždík, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
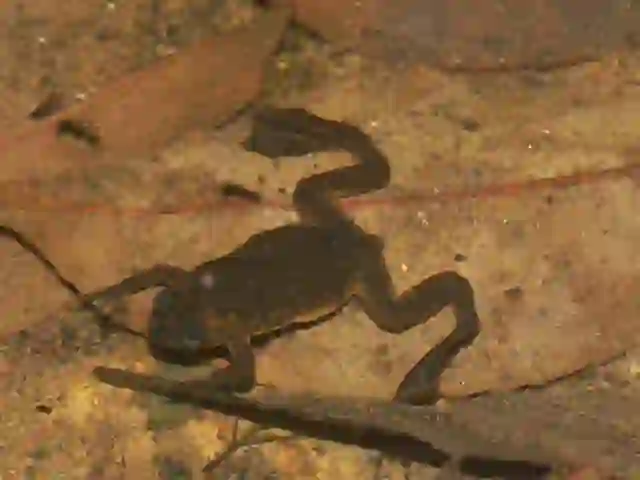

Václav Gvoždík, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons

Václav Gvoždík, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
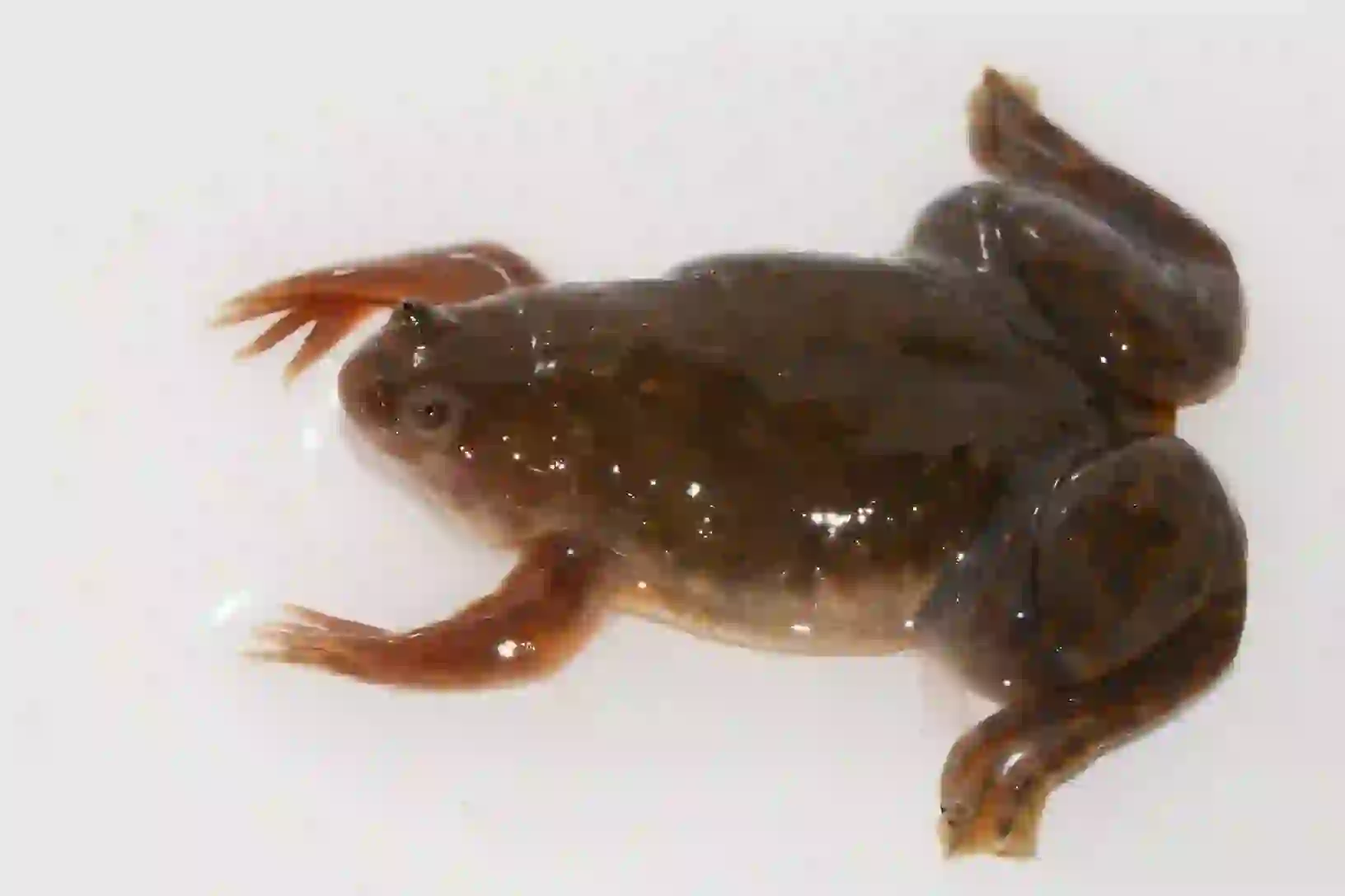

Marius Burger, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons

Brian Gratwicke from DC, USA, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons

Help Enrich Our Animalbook.jp with Your Media!
We are constantly looking to expand and enrich our Animalbook.jp with amazing photos and videos of animals. If you have any media that you'd like to share, please contribute and help us showcase the beauty and diversity of the animal kingdom. Your submissions will be credited and featured in our encyclopedia, reaching a wide audience of animal lovers.


















